what does it feel like to be in shock
The give-and-take shock can describe several different situations. Medical shock happens when the body'southward cells exercise not go enough oxygen-rich blood. It is not a disease just a issue of an affliction or injury.
A person may also feel shocked when they experience something unexpected. This stupor is psychological and usually does not cause any medical bug.
Another blazon of shock is an electric shock, which occurs when a person sustains an injury as a outcome of exposure to electrical energy. Causes of an electric stupor include faulty electrical equipment, lightning strikes, and contact with electricity and water.
Although many different problems can cause medical stupor, its symptoms are oft the aforementioned. Medical shock is always an emergency. Without treatment, shock may cause permanent organ harm or expiry.
There are four dissimilar types of medical stupor. The name of each type describes how it causes a decrease in blood menstruation to the cells and tissues.
The 4 types are:
- Hypovolemic shock. Hypovolemia is a decreased volume of blood in the body, and it may happen if a person is haemorrhage heavily or becomes severely dehydrated. This type of shock is
unremarkably due to severe blood loss following a traumatic injury. - Cardiac daze (too known equally cardiogenic shock). This type of shock occurs when the eye is unable to pump plenty blood. The causes of cardiac shock include a eye attack, heart failure, astringent blood loss, or an injury to the chest that damages the heart.
- Obstructive shock. Obstructive daze happens when a blockage in the cardiovascular system, such every bit a pulmonary embolism, keeps blood from flowing to the body'southward tissues and organs.
- Distributive shock (likewise known every bit vasodilatory shock). In distributive shock, fluid may collect between the cells of the organs, making it difficult for the blood to attain the tissues. The
most common causes of distributive shock include anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction, and sepsis. Poisoning or toxicity from drugs tin also cause this type of daze.
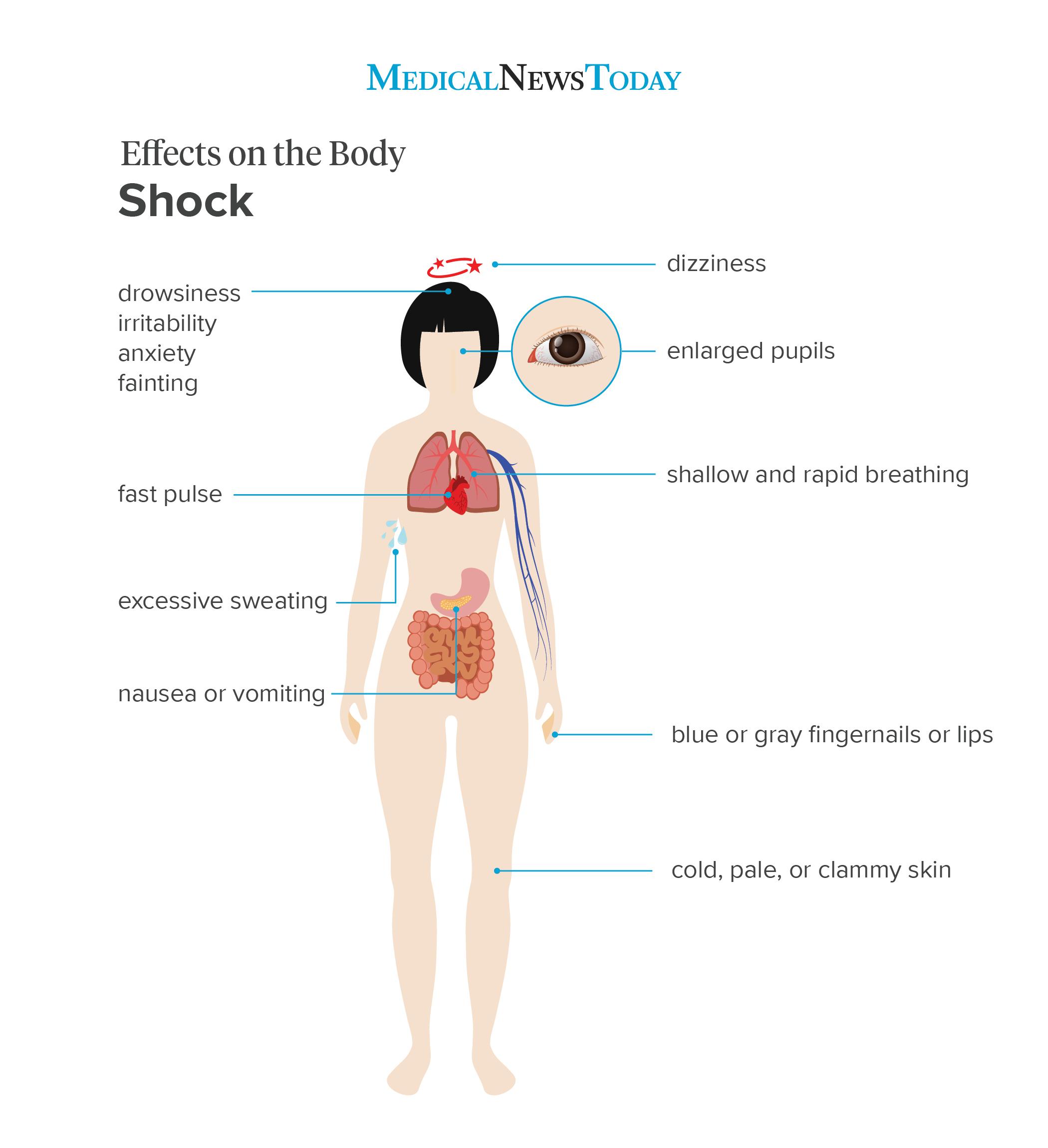
Although medical stupor has many unlike causes, its symptoms are generally the aforementioned. The symptoms are a result of the torso'due south organs and tissues non getting enough oxygen.
Signs and symptoms of shock include:
- cold, pale, or clammy skin
- excessive sweating
- fast middle charge per unit
- shallow and rapid breathing
- drowsiness
- fainting
- blue or grey lips or fingernails
- irritability
- anxiety
- dizziness
- enlarged pupils
- nausea or vomiting
If a person is in shock, the first step is to call 911 or the local emergency number, even if the symptoms are mild.
While waiting for the medical team, people tin can assist by:
- helping the person lie downwardly and elevate their anxiety, if possible
- avoiding moving the person if they may have injured their head, neck, or back
- performing beginning help on injuries if necessary
- keeping the person warm with a blanket or glaze
- refraining from giving the person food or drink
- checking for breathing and a pulse at least every five minutes (if the person is non animate, a trained person tin perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR))
- turning the person on their side if they are choking or airsickness
Medical professionals often recognize shock because of its feature signs, including low claret pressure.
The handling for shock will vary based on the underlying cause. For example, a person experiencing anaphylaxis may need a shot of epinephrine, which can treat astringent allergic reactions.
If a person has sepsis, they may need antibiotics, oxygen, and intravenous (Iv) fluids.
People with hypovolemic daze may need a claret transfusion and 4 fluids. Doctors may start blood transfusions or other measures to assistance restore proper blood catamenia, even if they exercise not know the underlying cause.
The medical team may run various tests to decide the cause of shock, including:
- X-rays
- blood tests
- urine tests
- CT scans
After a person receives handling for shock, a dr. may help them put a follow-up plan in place to help prevent some other effect. Some examples include:
- People who have cardiogenic daze due to a blood clot may need boosted treatment to break upwards the jell.
- A person who went into anaphylactic shock may need to bear epinephrine or other medications to help stop allergic reactions. They will likewise demand to avoid contact with allergens in the future.
- A person who had a heart attack may crave lifestyle changes and medications to help reduce the chances of another heart attack.
Information technology tin take some time to recover from any blazon of medical shock. Shock can cause fatigue, musculus aches, and trouble with forcefulness or mental part. Sometimes, these effects are long lasting.
People may need rehabilitation, either in the hospital or in another facility. They may too need aid with tasks at domicile every bit they recover.
After septic shock, some people feel lingering side effects, such as hurting or trouble concentrating or remembering things. Depression or anxiety may also occur. Talking to a doctor about these effects can assistance during recovery.
Medical stupor is a life threatening condition. Information technology occurs when the organs in the body are not getting enough oxygen.
Causes of shock include astringent blood loss, dehydration, and a cardiac event. It is important to seek firsthand medical care for any symptoms of shock, even if they are mild.
hagenauersorpathey1961.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326959